Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage
Mapping Genes
Problem 11
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIn the cross shown here, involving two linked genes, ebony (e) and claret (ca), in Drosophila, where crossing over does not occur in males, offspring were produced in a 2 + : 1 ca : 1 e phenotypic ratio:
These genes are 30 units apart on chromosome III. What did crossing over in the female contribute to these phenotypes? 
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Linked Genes
Linked genes are genes that are located close to each other on the same chromosome and tend to be inherited together during meiosis. Their proximity reduces the likelihood of recombination occurring between them, which can affect the phenotypic ratios observed in offspring. In the case of Drosophila, the genes ebony (e) and claret (ca) are linked, influencing the inheritance patterns seen in the cross.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Sex-Linked Genes
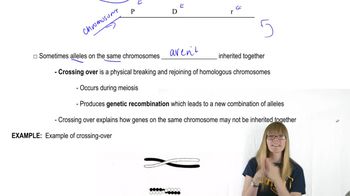
Crossing Over
Crossing over is a genetic process that occurs during meiosis where homologous chromosomes exchange segments of genetic material. This recombination can create new allele combinations, leading to genetic diversity in the offspring. In the context of the question, crossing over in females contributes to the observed phenotypic ratios by allowing for the production of recombinant gametes, which can result in different combinations of the linked genes.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Discovery of Crossing Over
Genetic Mapping
Genetic mapping is a technique used to determine the relative positions of genes on a chromosome based on the frequency of recombination between them. The distance between genes is often measured in centimorgans (cM), with 1 cM corresponding to a 1% chance of recombination occurring. In this scenario, the genes ebony and claret are 30 units apart, indicating a moderate likelihood of crossing over, which affects the phenotypic ratios of the offspring.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Mapping Overview
Related Videos
Related Practice





