Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
20. Quantitative Genetics
QTL Mapping
Problem 29b
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIn 1988, Horst Wilkens investigated blind cavefish, comparing them with members of a sibling species with normal vision that are found in a lake [Wilkens, H. (1988). Evol. Biol. 25:271–367]. We will call them cavefish and lakefish. Wilkens found that cavefish eyes are about seven times smaller than lakefish eyes. F₁ hybrids have eyes of intermediate size. These data, as well as the F₁×F₁ cross and those from backcrosses (F₁×cavefish and F₁×lakefish), are depicted below. Examine Wilkens's results and respond to the following questions: Wilkens examined about 1000 F₂ progeny and estimated that 6–7 genes are involved in determining eye size. Is the sample size adequate to justify this conclusion? Propose an experimental protocol to test the hypothesis.
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Genetic Inheritance
Genetic inheritance refers to the process by which traits and characteristics are passed from parents to offspring through genes. In the context of the cavefish and lakefish, understanding how eye size is inherited is crucial, as it involves multiple genes that contribute to phenotypic variation. The study of F₁ hybrids and their F₂ progeny helps illustrate how traits can segregate and combine in subsequent generations.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Diploid Genetics
Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL)
Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) are regions of the genome that are associated with the variation in a quantitative trait, such as eye size in fish. The identification of 6-7 genes influencing eye size suggests that this trait is polygenic, meaning it is controlled by multiple genes, each contributing to the overall phenotype. Understanding QTL is essential for designing experiments to map these genes and their effects on eye size.
Recommended video:
Guided course

QTL Mapping
Sample Size and Statistical Power
Sample size and statistical power are critical in experimental design, as they determine the reliability of the conclusions drawn from data. A sample size of about 1000 F₂ progeny is generally considered adequate for detecting genetic effects, but the power to detect specific gene interactions or effects may vary. Evaluating whether the sample size justifies Wilkens's conclusion about the number of genes involved requires understanding statistical methods and the expected effect sizes.
Recommended video:
Guided course
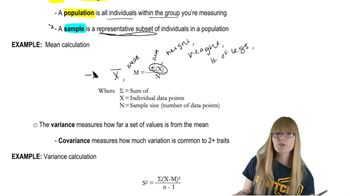
Mathematical Measurements
Related Videos
Related Practice




