Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance
Epistasis and Complementation
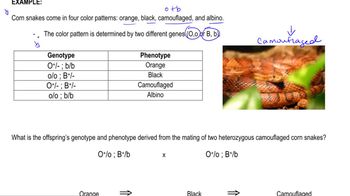
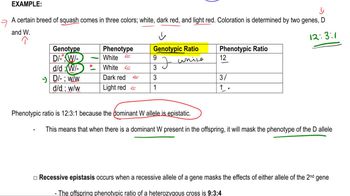
Problem 19b
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionFeather color in parakeets is produced by the blending of pigments from two biosynthetic pathways shown below. Four independently assorting genes (A, B, C, and D) produce enzymes that catalyze separate steps of the pathways. For the questions below, use an uppercase letter to indicate a dominant allele producing full enzymatic activity and a lowercase letter to indicate a recessive allele producing no functional enzyme. Feather colors produced by mixing pigments are green (yellow + blue) and purple (red + blue). Red, yellow, and blue feathers result from production of one colored pigment, and white results from absence of pigment production.

What is the genotype of a pure-breeding yellow strain of parakeet?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
336
views
Was this helpful?