Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination
DNA Repair
Problem 36c
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionA geneticist searching for mutations uses the restriction endonucleases SmaI and PvuII to search for mutations that eliminate restriction sites. SmaI will not cleave DNA with CpG methylation. It cleaves DNA at the restriction digestion sequence ↓ 5′−CCC GGG−3′ 3′−GGG CCC−3′ ↑ PvuII is not sensitive to CpG methylation. It cleaves DNA at the restriction sequence ↓ 5′−CAG CTG−3′ 3′−GTC GAC−5′ ↑ What common feature do SmaI and PvuII share that would be useful to a researcher searching for mutations that disrupt restriction digestion?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Restriction Endonucleases
Restriction endonucleases, or restriction enzymes, are proteins that cut DNA at specific sequences, known as restriction sites. Each enzyme recognizes a unique sequence of nucleotides and cleaves the DNA at or near this site. Understanding how these enzymes function is crucial for geneticists, as they can be used to analyze DNA fragments and identify mutations that may disrupt these specific sequences.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Mapping with Markers
Methylation and Its Effects
DNA methylation is a biochemical process involving the addition of a methyl group to the DNA molecule, often affecting gene expression and the ability of restriction enzymes to cleave DNA. For instance, SmaI is inhibited by CpG methylation, meaning it cannot cut DNA at its recognition site if that site is methylated. Recognizing how methylation influences enzyme activity is essential for understanding how mutations can affect restriction digestion.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Maternal Effect
Common Features of Restriction Enzymes
Despite their differences in sensitivity to methylation, SmaI and PvuII share the common feature of recognizing specific palindromic DNA sequences for cleavage. This characteristic allows researchers to utilize these enzymes to identify mutations that disrupt these sequences, as any alteration could prevent the enzyme from binding and cutting the DNA. Understanding this shared feature is vital for geneticists searching for mutations that affect restriction digestion.
Recommended video:
Guided course
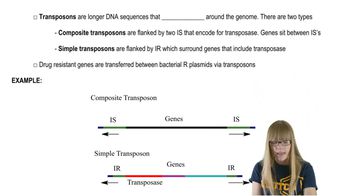
Prokaryotic Transposable Elements

 1:45m
1:45mWatch next
Master DNA Proofreading with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learning




