Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes
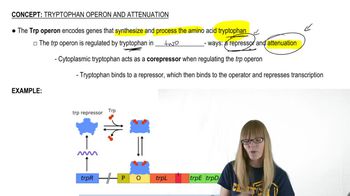
Tryptophan Operon and Attenuation
Problem 32a
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionSection 9.4 describes the function of tRNA synthetases in attaching amino acids to tRNAs (see Figure 9.16). Suppose the tRNA synthetase responsible for attaching tryptophan to tRNA is mutated in a bacterial strain with the result that the tRNA synthetase functions at about 15% of the efficiency of the wild-type tRNA synthetase. Would formation of the 3–4 stem-loop structure in mRNA be more frequent or less frequent in the mutant strain than in the wild-type strain? Why?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
6mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
tRNA Synthetases
tRNA synthetases are enzymes that play a crucial role in protein synthesis by attaching specific amino acids to their corresponding transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules. Each tRNA synthetase is specific to one amino acid and its associated tRNA, ensuring that proteins are synthesized accurately according to the genetic code. A mutation that reduces the efficiency of a tRNA synthetase can lead to decreased availability of the corresponding amino acid for protein synthesis.
Recommended video:
Stem-Loop Structures in mRNA
Stem-loop structures in mRNA are formed when complementary sequences within the RNA strand base-pair with each other, creating a loop and a double-stranded stem. These structures can play significant roles in the regulation of gene expression, including the termination of transcription and the modulation of translation. The frequency of stem-loop formation can be influenced by the availability of tRNAs and the efficiency of amino acid incorporation during protein synthesis.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Ribosome Structure
Impact of Mutations on Gene Expression
Mutations in genes encoding proteins, such as tRNA synthetases, can significantly affect cellular processes, including gene expression and protein synthesis. A mutation that reduces the function of a tRNA synthetase may lead to a shortage of the corresponding amino acid, potentially causing ribosomes to stall during translation. This stalling can influence the formation of secondary structures in mRNA, such as stem-loops, by altering the timing and efficiency of translation.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Penetrance and Expressivity