Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
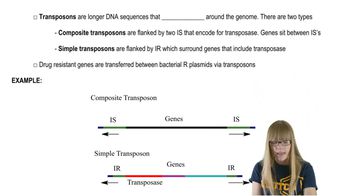
Transposons
Transposons, or 'jumping genes,' are DNA sequences that can change their position within the genome. They can cause mutations by inserting themselves into or near genes, potentially disrupting normal gene function or regulatory elements. Understanding transposons is crucial for predicting the types of mutations they may induce during experiments, such as enhancer trapping.
Recommended video:
Prokaryotic Transposable Elements
Enhancer Elements
Enhancers are regulatory DNA sequences that can increase the likelihood of transcription of specific genes. They can function over long distances and are often located upstream or downstream of the genes they regulate. In the context of transposon experiments, enhancers can activate the expression of a reporter gene, leading to various mutations depending on their interaction with nearby genes.
Recommended video:
Mutagenesis
Mutagenesis refers to the process by which genetic information is changed, resulting in mutations. In the context of transposon-induced mutagenesis, the insertion of a transposon can lead to various types of mutations, including insertions, deletions, and point mutations. Understanding mutagenesis is essential for predicting the outcomes of experiments that utilize transposons to manipulate gene expression.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution