Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes
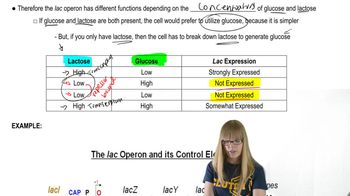
Lac Operon
Problem 22d
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionThe SOS repair genes in E. coli (discussed in Chapter 15) are negatively regulated by the lexA gene product, called the LexA repressor. When a cell's DNA sustains extensive damage, the LexA repressor is inactivated by the recA gene product (RecA), and transcription of the SOS genes is increased dramatically. One of the SOS genes is the uvrA gene. You are a student studying the function of the uvrA gene product in DNA repair. You isolate a mutant strain that shows constitutive expression of the UvrA protein. Naming this mutant strain uvrAᶜ, you construct the diagram shown above in the right-hand column showing the lexA and uvrA operons: Describe two different mutations that would result in a uvrA constitutive phenotype. Indicate the actual genotypes involved. (Leader sequence for Problem 24 above)
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
418
views
Was this helpful?
Related Videos
Related Practice