Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
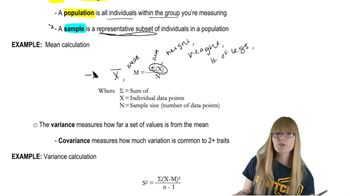
20. Quantitative Genetics
Mathematical Measurements
Problem 21
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionA 3-inch plant was crossed with a 15-inch plant, and all F₁ plants were 9 inches. The F₂ plants exhibited a 'normal distribution,' with heights of 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15 inches.
What ratio will constitute the 'normal distribution' in the F₂?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Normal Distribution
Normal distribution is a statistical concept where data points are symmetrically distributed around a mean, forming a bell-shaped curve. In genetics, traits often follow this distribution when influenced by multiple genes, leading to a range of phenotypes. The heights of the F₂ plants in this scenario suggest that multiple alleles contribute to the trait, resulting in a continuous variation of plant heights.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Cell-cell interactions
F₁ and F₂ Generations
The F₁ generation is the first filial generation resulting from a cross between two parental (P) plants, while the F₂ generation is produced by interbreeding F₁ individuals. In this case, the F₁ plants are all 9 inches tall, indicating a dominant trait, while the F₂ generation shows a range of heights, reflecting the segregation of alleles and the reappearance of the parental traits.
Recommended video:
Guided course

F Factor and Hfr
Phenotypic Ratio
Phenotypic ratio refers to the relative frequency of different phenotypes in a population. In the context of the F₂ generation, the normal distribution of plant heights suggests that the phenotypic ratio will not be a simple Mendelian ratio (like 3:1 or 9:3:3:1) but rather a continuous range of heights. This indicates polygenic inheritance, where multiple genes influence a single trait.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Mutations and Phenotypes

 11:1m
11:1mWatch next
Master Mathematical Measurements with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice