Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance
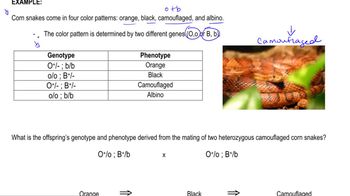
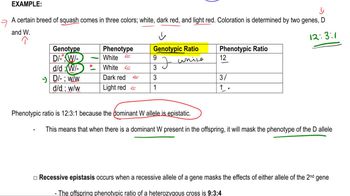
Epistasis and Complementation
Problem 10a
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionA researcher interested in studying a human gene on chromosome 21 and another gene on the X chromosome uses FISH probes to locate each gene. The chromosome 21 probe produces green fluorescent color, and the X chromosome probe produces red fluorescent color.
If the subject studied is male, how many green and red spots will be detected? Explain your answer.
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Chromosome Structure and Function
Chromosomes are structures within cells that contain DNA, which carries genetic information. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, including one pair of sex chromosomes (XX for females and XY for males). Each chromosome can carry multiple genes, and their arrangement is crucial for proper gene expression and inheritance.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chromosome Structure
Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH)
FISH is a molecular cytogenetic technique used to detect and localize the presence or absence of specific DNA sequences on chromosomes. By using fluorescent probes that bind to specific genes, researchers can visualize the location of these genes under a fluorescence microscope, allowing for the identification of chromosomal abnormalities or gene mapping.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Functional Genomics
Sex Chromosomes and Gene Dosage
In humans, males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY), while females have two X chromosomes (XX). This difference in sex chromosome composition affects gene dosage; males have only one copy of genes located on the X chromosome, while females have two. Therefore, in a male subject, only one red spot (for the X chromosome gene) will be detected, while two green spots (for the chromosome 21 gene) will be observed, assuming there are two copies of that gene.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Human Sex Chromosomes

 5:05m
5:05mWatch next
Master Complementation with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learning