Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes
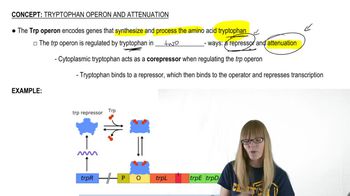
Tryptophan Operon and Attenuation
Problem 6
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIs attenuation the product of an allosteric effect? Is attenuation the result of a transcriptional or a translational activity? Explain your answers.
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Attenuation
Attenuation is a regulatory mechanism in gene expression, particularly in prokaryotes, where the transcription of a gene is prematurely terminated. This process is influenced by the formation of specific RNA structures during transcription, which can be affected by the availability of certain metabolites. It serves as a way for cells to conserve resources by halting the production of proteins when they are not needed.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Trp Attenuation
Allosteric Effect
An allosteric effect refers to the regulation of a protein's function through the binding of a molecule at a site other than the active site, leading to a conformational change. This can enhance or inhibit the protein's activity, impacting processes such as enzyme function or receptor signaling. In the context of attenuation, allosteric effects can influence the formation of RNA structures that determine whether transcription continues or stops.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Maternal Effect
Transcriptional vs. Translational Regulation
Transcriptional regulation involves controlling the synthesis of RNA from DNA, determining which genes are expressed and to what extent. In contrast, translational regulation pertains to the control of protein synthesis from mRNA. Attenuation primarily acts at the transcriptional level by affecting the continuation of RNA synthesis, although it can also have implications for translation depending on the RNA structures formed.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Translation initiation