Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes
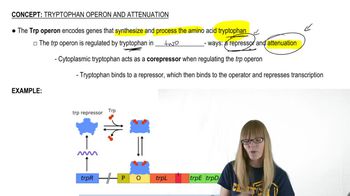
Tryptophan Operon and Attenuation
Problem 25g
Textbook Question
What is the likely effect of each of the following mutations of the trpL region on attenuation control of trp operon gene transcription? Explain your reasoning. Ten nucleotides are inserted between regions 2 and 3 of trpL.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the role of the trpL region in the trp operon. The trpL region contains sequences that form stem-loop structures, which are crucial for the attenuation mechanism controlling the transcription of the trp operon.
Identify the regions involved in attenuation. The trpL region has four segments (1, 2, 3, and 4) that can form alternative stem-loop structures. The pairing of regions 2 and 3 prevents the formation of the terminator structure between regions 3 and 4, allowing transcription to continue.
Consider the effect of inserting ten nucleotides between regions 2 and 3. This insertion could disrupt the normal base pairing between regions 2 and 3, potentially preventing the formation of the anti-terminator structure.
Predict the impact on transcription. If regions 2 and 3 cannot pair, the terminator structure between regions 3 and 4 may form more readily, leading to premature termination of transcription and reduced expression of the trp operon genes.
Conclude the likely effect. The insertion of nucleotides between regions 2 and 3 is likely to enhance attenuation, resulting in decreased transcription of the trp operon genes under conditions where attenuation is active.
Recommended similar problem, with video answer:
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Attenuation in Gene Regulation
Attenuation is a regulatory mechanism in prokaryotes, particularly in the trp operon, where transcription is prematurely terminated based on the availability of tryptophan. It involves the formation of specific RNA structures that determine whether transcription continues or halts. This process is crucial for fine-tuning gene expression in response to metabolic needs.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Trp Attenuation
trp Operon Structure
The trp operon is a cluster of genes in bacteria that encode enzymes for tryptophan biosynthesis. It includes regulatory regions such as the leader sequence (trpL), which plays a key role in attenuation. The operon is controlled by the levels of tryptophan, influencing whether the operon is expressed or repressed.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Trp Attenuation
Mutations and Their Effects
Mutations, such as insertions or deletions in DNA, can significantly alter gene function and regulation. In the context of the trpL region, inserting ten nucleotides between regions 2 and 3 may disrupt the formation of the necessary RNA structures for proper attenuation. This could lead to either increased or decreased transcription of the trp operon, depending on how the mutation affects the ribosome's interaction with the mRNA.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Maternal Effect