Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes
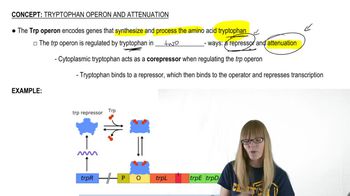
Tryptophan Operon and Attenuation
Problem 25i
Textbook Question
What is the likely effect of each of the following mutations of the trpL region on attenuation control of trp operon gene transcription? Explain your reasoning. Two nucleotides are inserted into the trpL region immediately after the polypeptide stop codon.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the role of the trpL region in the trp operon. The trpL region contains the leader peptide sequence and is involved in the attenuation mechanism, which regulates the transcription of the trp operon based on tryptophan levels.
Understand the concept of attenuation. Attenuation is a regulatory mechanism where the formation of a transcription terminator structure in the mRNA can halt transcription prematurely, depending on the availability of tryptophan.
Consider the effect of inserting two nucleotides after the stop codon in the trpL region. This insertion could potentially disrupt the normal formation of the mRNA secondary structure, which is crucial for attenuation control.
Analyze how the insertion might affect the formation of the terminator or antiterminator structures. The insertion could cause a frameshift in the mRNA sequence, altering the ability of the ribosome to pause correctly, which is necessary for the formation of the antiterminator structure when tryptophan is scarce.
Predict the likely outcome on transcription. If the insertion disrupts the normal attenuation mechanism, it could lead to either constitutive expression or repression of the trp operon, depending on whether the terminator or antiterminator structure is affected.
Recommended similar problem, with video answer:
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Attenuation Control
Attenuation is a regulatory mechanism in prokaryotic gene expression, particularly in the trp operon, where the formation of specific RNA structures determines whether transcription continues or terminates. In the trp operon, the leader sequence (trpL) contains regions that can form alternative secondary structures, influencing the transcription process based on tryptophan levels.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Trp Attenuation
trp Operon
The trp operon is a cluster of genes in bacteria that encode enzymes for tryptophan biosynthesis. It is regulated by both repression and attenuation mechanisms, allowing the cell to efficiently manage tryptophan production in response to its availability. Mutations in this operon can significantly affect its expression and the organism's ability to synthesize tryptophan.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Trp Attenuation
Mutations and Their Effects
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence that can alter gene function. In the context of the trpL region, inserting nucleotides can disrupt the normal formation of RNA secondary structures, potentially leading to premature termination of transcription or altered regulation of the trp operon. Understanding the specific effects of these mutations is crucial for predicting changes in gene expression.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Maternal Effect