Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
6. Chromosomal Variation
Chromosomal Mutations: Aneuploidy
Problem 26
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIn a recent cytogenetic study on 1021 cases of Down syndrome, 46 were the result of translocations, the most frequent of which was symbolized as t(14;21). What does this symbol represent, and how many chromosomes would you expect to be present in t(14;21) Down syndrome individuals?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Translocation
Translocation is a genetic phenomenon where a segment of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome. In the context of Down syndrome, a specific type of translocation can lead to the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21, which is responsible for the condition. The notation t(14;21) indicates that a piece of chromosome 21 has been translocated to chromosome 14.
Recommended video:
Guided course
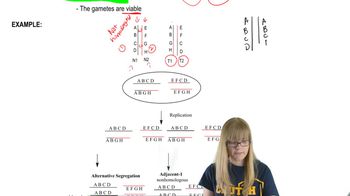
Reciprocal Translocation
Chromosome Count in Down Syndrome
Individuals with Down syndrome typically have 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46 due to the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21. In cases of translocation Down syndrome, such as t(14;21), the total chromosome count remains 47, as the translocated segment does not create an additional full chromosome but rather alters the structure of existing ones.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Human Sex Chromosomes
Cytogenetics
Cytogenetics is the branch of genetics that studies the structure and function of chromosomes. It involves analyzing chromosomal abnormalities, such as those seen in Down syndrome, to understand their implications for health and development. Cytogenetic studies often utilize techniques like karyotyping to visualize and identify chromosomal changes, including translocations.
Related Videos
Related Practice




