Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
7. DNA and Chromosome Structure
DNA Structure
Problem 25
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionWhat did the Watson–Crick model suggest about the replication of DNA?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Watson-Crick Model
The Watson-Crick model, proposed by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953, describes the double helix structure of DNA. It illustrates how two strands of DNA are held together by complementary base pairing between adenine-thymine and guanine-cytosine. This model is fundamental for understanding how genetic information is stored and transmitted.
Recommended video:
Guided course

History and Experiments
Semi-conservative Replication
The semi-conservative replication mechanism, as suggested by the Watson-Crick model, indicates that during DNA replication, each new DNA molecule consists of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand. This process ensures that genetic information is accurately passed on to daughter cells, maintaining the integrity of the genetic code across generations.
Recommended video:
Guided course
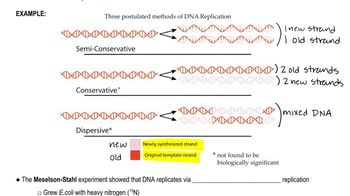
Semiconservative Replication
Base Pairing
Base pairing refers to the specific hydrogen bonding between nucleotide bases in DNA, where adenine pairs with thymine and guanine pairs with cytosine. This complementary pairing is crucial for the accurate replication of DNA, as it ensures that each new strand is an exact copy of the original, facilitating the faithful transmission of genetic information.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Base Distortions
Related Videos
Related Practice




