Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
9. Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitosis
Problem 1d
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionExamine the following diagrams of cells from an organism with diploid number 2n=6, and identify what stage of M phase is represented.
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
58sPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
M Phase
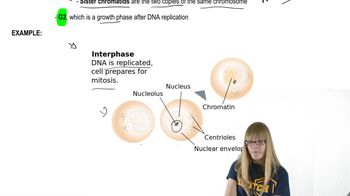
M Phase, or mitotic phase, is the stage of the cell cycle where cell division occurs. It includes both mitosis, the process of nuclear division, and cytokinesis, the division of the cytoplasm. Understanding M Phase is crucial for identifying the specific stage represented in the diagrams, as it encompasses several distinct phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Cancer Causes
Diploid Number
The diploid number (2n) refers to the total number of chromosomes in a somatic cell, where chromosomes exist in pairs. In this case, 2n=6 indicates that the organism has six chromosomes, or three pairs. Recognizing the diploid number helps in understanding the genetic makeup of the organism and the implications for chromosome behavior during M Phase.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Diploid Genetics
Chromosome Structure During M Phase
During M Phase, chromosomes undergo significant structural changes, becoming highly condensed and visible under a microscope. Each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids joined at the centromere. Identifying the arrangement and number of chromatids in the diagrams is essential for determining the specific stage of M Phase, as the appearance of chromosomes varies between prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chromosome Structure
Related Videos
Related Practice