Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance
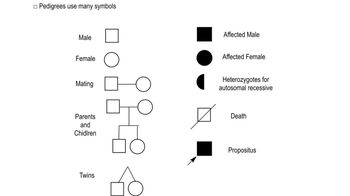
Pedigrees
Problem 40a
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionThe following pedigree is characteristic of an inherited condition known as male precocious puberty, where affected males show signs of puberty by age 4. Propose a genetic explanation of this phenotype.
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance
Autosomal dominant inheritance occurs when a single copy of a mutated gene from one parent is sufficient to cause a phenotype. In the case of male precocious puberty, if the condition is inherited in this manner, affected males would have a 50% chance of passing the trait to their offspring. This pattern can often be traced through a pedigree, showing affected individuals in multiple generations.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Variations on Dominance
Sex-Linked Traits
Sex-linked traits are associated with genes located on sex chromosomes, typically the X chromosome. In males, who have one X and one Y chromosome, any mutation on the X chromosome can manifest as a phenotype. Understanding whether the condition is linked to the X chromosome can help explain its inheritance pattern, especially if it shows a higher prevalence in males.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Sex-Linked Genes
Gene Mutation and Phenotype Expression
Gene mutations can lead to abnormal protein function, which may result in specific phenotypes, such as early onset of puberty. In the case of male precocious puberty, mutations in genes regulating hormonal pathways could lead to premature activation of puberty-related processes. Identifying the specific gene involved can provide insights into the biological mechanisms underlying this condition.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Mutations and Phenotypes

 2:48m
2:48mWatch next
Master Pedigree Symbols with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learning