Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
6. Chromosomal Variation
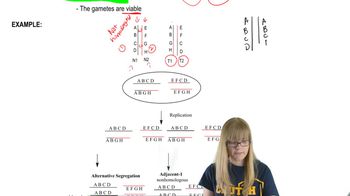
Chromosomal Rearrangements: Translocations
Problem 24b
Textbook Question
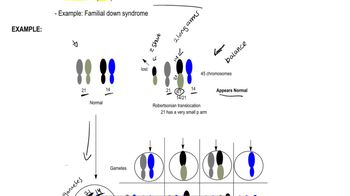
Textbook QuestionA boy with Down syndrome (trisomy 21) has 46 chromosomes. His parents and his two older sisters have a normal phenotype, but each has 45 chromosomes.
What term best describes this kind of chromosome abnormality?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Chromosome Number Abnormalities
Chromosome number abnormalities occur when there is a deviation from the normal diploid number of chromosomes, which is 46 in humans. These abnormalities can manifest as aneuploidy, where there is an extra or missing chromosome, or polyploidy, where there are multiple sets of chromosomes. In the case of Down syndrome, the individual has an extra copy of chromosome 21, leading to trisomy 21.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Human Sex Chromosomes
Aneuploidy
Aneuploidy is a specific type of chromosome number abnormality characterized by the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell. This can include conditions such as monosomy (one less chromosome) or trisomy (one extra chromosome). In the context of the question, the boy with Down syndrome has trisomy 21, indicating he has three copies of chromosome 21 instead of the usual two.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Aneuploidy
Phenotype vs. Genotype
Phenotype refers to the observable physical and physiological traits of an organism, while genotype refers to the genetic makeup that determines these traits. In the scenario presented, the boy with Down syndrome has a distinct phenotype associated with his condition, despite having a normal chromosome count of 46. His parents and sisters, with 45 chromosomes, may exhibit a normal phenotype, suggesting they could be carriers of a chromosomal abnormality without expressing it.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Gamete Genotypes

 12:42m
12:42mWatch next
Master Reciprocal Translocation with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice