Textbook Question
Write a nuclear equation for the indicated decay of each nuclide. a. U-234 (alpha) b. Th-230 (alpha)
970
views
1
rank
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

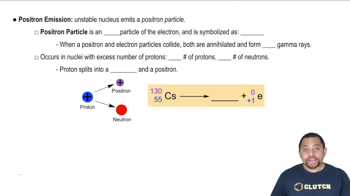

Write a nuclear equation for the indicated decay of each nuclide. a. U-234 (alpha) b. Th-230 (alpha)
Write a nuclear equation for the indicated decay of each nuclide. c. Pb-214 (beta)
Write a nuclear equation for the indicated decay of each nuclide. e. Cr-51 (electron capture)
Write a nuclear equation for the indicated decay of each nuclide. a. Po-210 (alpha) b. Ac-227 (beta)
Write a nuclear equation for the indicated decay of each nuclide.
c. Tl-207 (beta)