Predict the ordering, from shortest to longest, of the bond lengths in CO, CO2, and CO32- .
b. Which of these compounds or ions is an exception to the octet rule: nitrogen dioxide, borohydride (BH4−), borazine (B3N3H6 which is analogous to benzene with alternating B and N in the ring), or boron trichloride?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Octet Rule

Exceptions to the Octet Rule

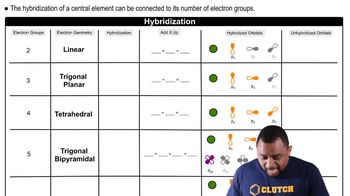
Molecular Geometry and Hybridization
Consider a Lewis structure for SO3 that satisfies the octet rule. Which of the following statements is or are true?
i. SO3 has three equivalent resonance structures.
ii. There are one shorter and two longer S—O bond lengths in SO3.
iii. The S atom in SO3 has a nonzero formal charge.
Which of the following statements about benzene, C6H6, is or are true?
i. Benzene has two equivalent resonance structures.
ii. There are no nonbonding pairs in the Lewis structure for benzene.
iii. Benzene has three short and three long C—C bonds.
Draw the Lewis structures for each of the following molecules or ions. Identify instances where the octet rule is not obeyed; state which atom in each compound does not follow the octet rule; and state how many electrons surround these atoms: a. NO, b. BF3, c. ICl2−, d. OPBr3 (the P is the central atom), e. XeF4.
