Textbook Question
(b) Calculate the percent ionization of 0.125 M lactic acid in a solution containing 0.0075 M sodium lactate.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


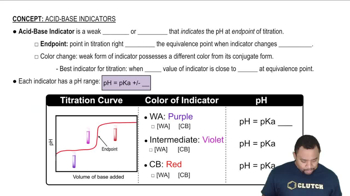
(b) Calculate the percent ionization of 0.125 M lactic acid in a solution containing 0.0075 M sodium lactate.
Which of the following solutions is a buffer? (a) A solution made by mixing 100 mL of 0.100 M CH3COOH and 50 mL of 0.100 M NaOH, (b) a solution made by mixing 100 mL of 0.100 M CH3COOH and 500 mL of 0.100 M NaOH, (c) A solution made by mixing 100 mL of 0.100 M CH3COOH and 50 mL of 0.100 M HCl, (d) A solution made by mixing 100 mL of 0.100 M CH3COOK and 50 mL of 0.100 M KCl.
(b) Calculate the pH of a buffer formed by mixing 85 mL of 0.13 M lactic acid with 95 mL of 0.15 M sodium lactate.