Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
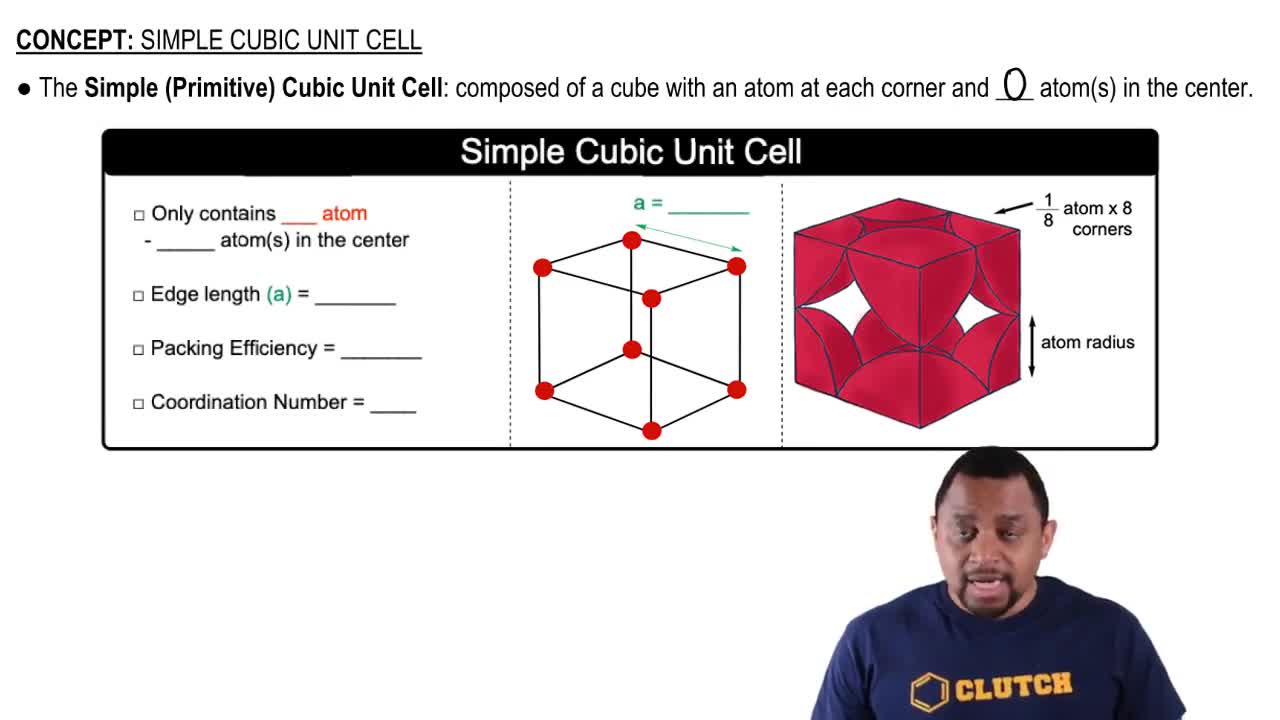
Unit Cell
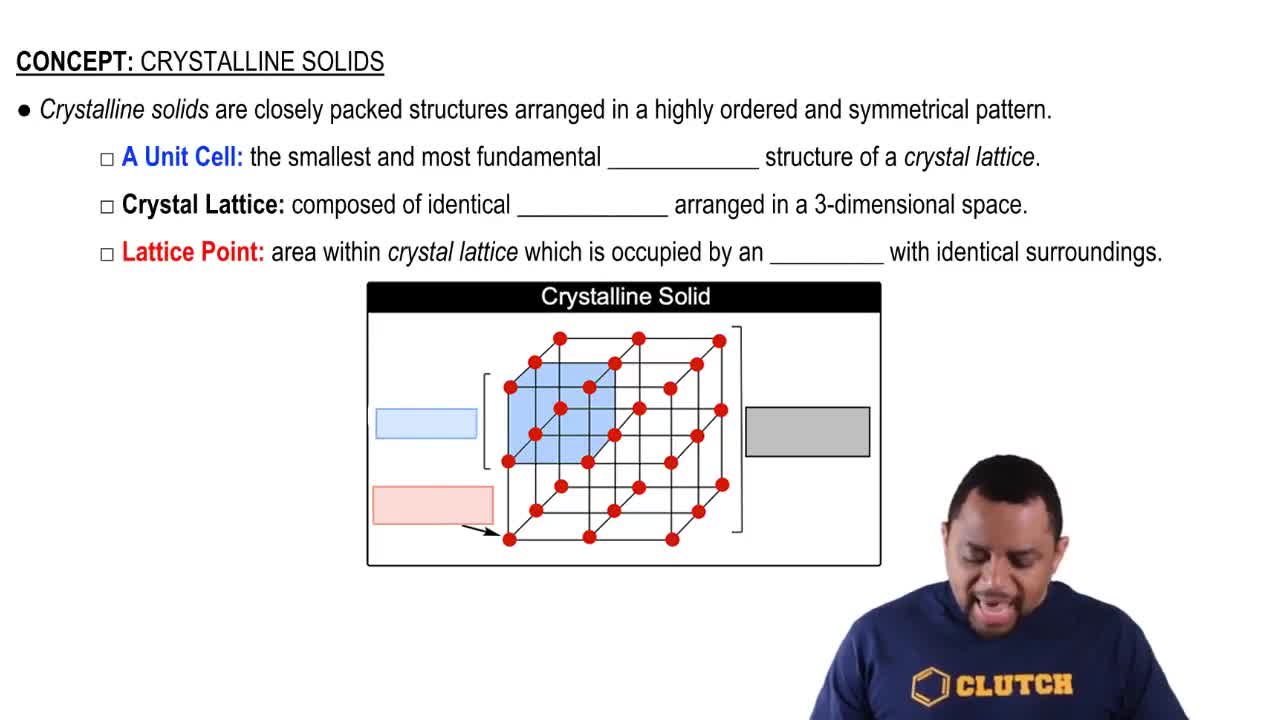
A unit cell is the smallest repeating unit of a crystal lattice that reflects the symmetry and structure of the entire crystal. It defines the arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in a crystalline solid. Understanding the unit cell is crucial for visualizing how the larger crystal structure is built and for calculating properties such as density and packing efficiency.
Recommended video:
Crystalline Structure
Crystalline structures are ordered arrangements of atoms or molecules in a solid, characterized by a repeating pattern. These structures can be classified into different types based on their symmetry and the arrangement of their unit cells, such as cubic, tetragonal, or hexagonal. Recognizing the type of crystalline structure is essential for predicting physical properties like melting point and conductivity.
Recommended video:
Crystalline Solids Structure
Coordination Number
The coordination number refers to the number of nearest neighbor atoms or ions surrounding a central atom in a crystal lattice. It is a key factor in determining the stability and properties of the crystal. For example, in a face-centered cubic structure, the coordination number is 12, indicating a high packing efficiency and stability, which influences the material's mechanical properties.
Recommended video:

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance