Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Acid Strength and Structure
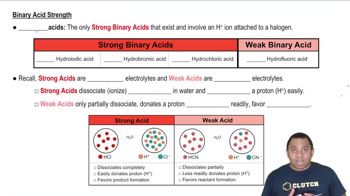
The strength of an acid is influenced by its molecular structure, particularly the electronegativity of atoms and the stability of the conjugate base. In oxyacids, the number of oxygen atoms bonded to the central atom typically increases acid strength, as more oxygen atoms can stabilize the negative charge on the conjugate base through resonance.
Recommended video:
Oxyacids
Oxyacids are acids that contain oxygen, hydrogen, and another element (the central atom). The general formula is HnXOm, where X is the central atom. The strength of oxyacids often increases with the number of oxygen atoms attached to the central atom, as these additional oxygens can help stabilize the conjugate base formed after deprotonation.
Recommended video:
Conjugate Base Stability
The stability of the conjugate base formed when an acid donates a proton is crucial in determining acid strength. A more stable conjugate base corresponds to a stronger acid. In the case of HBrO3 and HBrO2, the conjugate base of HBrO3 is more stable due to the presence of an additional oxygen atom, which allows for greater resonance stabilization.
Recommended video:
Strength of Conjugate Acids and Bases
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance