Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
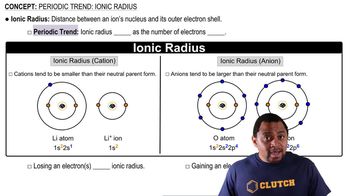
Ionic Radius
The ionic radius refers to the size of an ion in a crystal lattice. Smaller ions, like Li<sup>+</sup>, have a greater charge density, which allows them to interact more strongly with surrounding solvent molecules, such as water. This increased interaction leads to a higher solvation energy, making the ion-solvent interaction stronger compared to larger ions like K<sup>+</sup>.
Recommended video:
Charge Density
Charge density is defined as the amount of charge per unit volume. Cations with higher charge density, such as Li<sup>+</sup>, exert a stronger electrostatic attraction on polar solvent molecules like water. This results in more significant ion-dipole interactions, enhancing the solvation process compared to cations with lower charge density, like K<sup>+</sup>.
Recommended video:
Ion-Solvent Interactions
Ion-solvent interactions are the forces that occur between ions and solvent molecules. These interactions are crucial in determining the solubility and stability of ions in solution. The strength of these interactions is influenced by factors such as ionic size, charge, and the polar nature of the solvent, which in this case is water.
Recommended video: