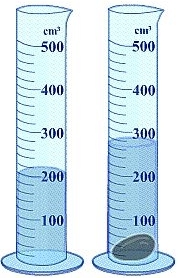
To calculate the density of non-geometric objects, the method of water displacement is employed. This technique involves measuring the volume of water that is displaced when an object is fully submerged in water. The principle behind this method is that the volume of water displaced is equal to the volume of the object submerged.
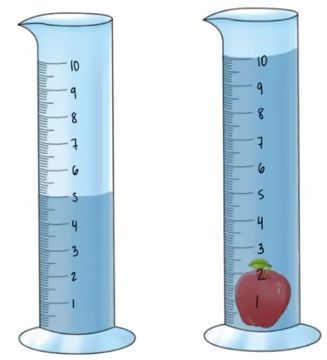
For instance, consider a scenario where we have a graduated cylinder filled with water. Initially, the water level is at approximately 3.5 milliliters (mL). When a non-geometric object is submerged, the water level rises. After submerging the object, the new water level reads approximately 5.8 mL. To find the volume of the object, we subtract the initial water volume from the final water volume:
Volume of the object = Final volume - Initial volume
Volume of the object = 5.8 mL - 3.5 mL = 2.3 mL
Thus, the volume of the non-geometric object is 2.3 milliliters. This method is particularly useful for objects that do not have a regular shape, allowing for accurate volume measurement through the displacement of water.
 1 student found this helpful
1 student found this helpful