Weak Titrate-Strong Titrant Curves definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackWeak Titrate-Strong Titrant Curves definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
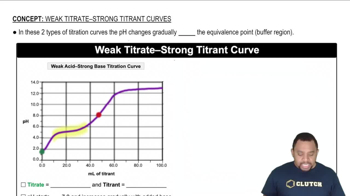
- Buffer RegionA section in a titration curve where pH changes gradually due to the presence of a buffer system.
- Half-Equivalence PointThe midpoint in the buffer region where the concentration of weak acid equals its conjugate base.
- Equivalence PointThe point in a titration curve with the steepest pH change, indicating equal moles of titrant and titrate.
- Weak AcidA substance that partially dissociates in solution, resulting in a pH less than 7 when titrated with a strong base.
- Strong BaseA substance that fully dissociates in solution, raising the pH above 7 when titrating a weak acid.
- Weak BaseA substance that partially dissociates in solution, resulting in a pH greater than 7 when titrated with a strong acid.
- Strong AcidA substance that fully dissociates in solution, lowering the pH below 7 when titrating a weak base.
- TitrantA solution of known concentration added to another solution to determine its concentration.
- TitrateA solution whose concentration is determined by titration with a titrant.
- pH PlateauThe stage in a titration curve where pH levels off after the equivalence point due to excess titrant.
- Conjugate BaseThe species formed when a weak acid donates a proton during a titration.
- pHA measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution, crucial in determining titration curve characteristics.
- Steepest InclineThe part of the titration curve where pH changes most rapidly, indicating the equivalence point.
- NeutralizationThe reaction between an acid and a base to form water and a salt, key in reaching the equivalence point.
- Excess TitrantThe additional titrant present after the equivalence point, causing further pH changes.