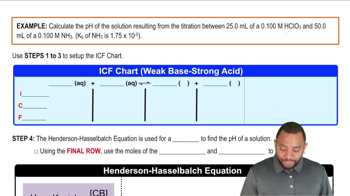
Titrations: Weak Base-Strong Acid definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackTitrations: Weak Base-Strong Acid definitions
1/11
Terms in this set (11)
- TitrationA laboratory method to determine the concentration of a solute in a solution by adding a titrant of known concentration.
- Weak BaseA base that does not completely ionize in solution, resulting in a higher pH than a strong base.
- Strong AcidAn acid that completely ionizes in solution, significantly lowering the pH.
- Equivalence PointThe stage in titration where the moles of acid equal the moles of base, resulting in neutralization.
- BufferA solution that resists changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added.
- Henderson-Hasselbalch EquationAn equation used to calculate the pH of a buffer solution using the concentration of acid and its conjugate base.
- ICF ChartA tool used to track the initial, change, and final amounts of reactants and products in a chemical reaction.
- MolarityA measure of the concentration of a solute in a solution, expressed as moles of solute per liter of solution.
- Conjugate AcidThe species formed when a base gains a proton, often present in buffer solutions.
- NeutralizationA chemical reaction in which an acid and a base react to form water and a salt, resulting in a neutral pH.
- IonizationThe process by which an atom or molecule gains or loses electrons to form ions, affecting pH.