The Colligative Properties definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackThe Colligative Properties definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- Colligative PropertiesProperties of solutions that depend on the number of solute particles, not their identity.
- Boiling PointTemperature at which a liquid's vapor pressure equals the external pressure, causing it to vaporize.
- Freezing PointTemperature at which a liquid becomes solid, with equilibrium between solid and liquid phases.
- Vapor PressurePressure exerted by a vapor in equilibrium with its liquid at a given temperature.
- Osmotic PressureForce driving water movement from low to high solute concentration through a semipermeable membrane.
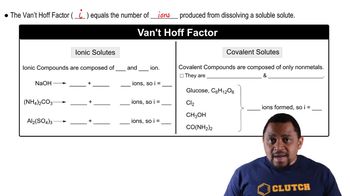
- Van't Hoff FactorNumber of particles a solute dissociates into in solution, affecting colligative properties.
- Ionic CompoundsCompounds that dissociate into ions in solution, affecting colligative properties significantly.
- Covalent CompoundsNon-electrolyte compounds that do not dissociate into ions in solution.
- OsmolarityConcentration of solute particles in a solution, considering ionic dissociation.
- OsmolalityConcentration of solute particles per kilogram of solvent, considering ionic dissociation.
- MolarityConcentration of a solute in a solution expressed as moles per liter.
- MolalityConcentration of a solute in a solution expressed as moles per kilogram of solvent.
- EquilibriumState where opposing processes occur at equal rates, maintaining a stable system.
- Non-electrolytesSubstances that do not dissociate into ions in solution, typically covalent compounds.
- SoluteSubstance dissolved in a solvent to form a solution, affecting colligative properties.