Test for Ions and Gases definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackTest for Ions and Gases definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- AnionsNegatively charged ions that can be identified through specific chemical tests.
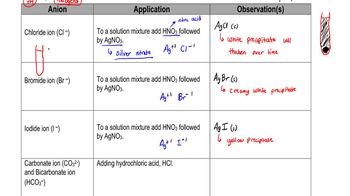
- Chloride IonForms a white precipitate of silver chloride when reacted with nitric acid and silver nitrate.
- Bromide IonProduces a creamy white precipitate of silver bromide with nitric acid and silver nitrate.
- Iodide IonResults in a yellow precipitate of silver iodide when combined with nitric acid and silver nitrate.
- Carbonate IonReacts with hydrochloric acid to produce carbon dioxide gas and forms a white precipitate with magnesium sulfate.
- Bicarbonate IonAlso known as hydrogen carbonate, it releases carbon dioxide gas with hydrochloric acid but no precipitate with magnesium sulfate.
- Sulfate IonForms a white precipitate of barium sulfate with barium chloride and requires strong heating to release sulfur trioxide gas.
- Bisulfate IonProduces sulfur trioxide gas with light heating and releases more CO2 with sodium carbonate.
- Sulfide IonReleases sulfur dioxide gas with a strong odor when reacted with hydrochloric acid.
- Nitrate IonIdentified by the brown ring test, forming a brown ring with cold iron(II) sulfate and sulfuric acid.
- PrecipitateA solid formed in a solution during a chemical reaction, indicating the presence of specific ions.
- Silver NitrateReagent used to detect halide ions by forming distinct colored precipitates.
- Nitric AcidUsed in combination with silver nitrate to test for halide ions in a solution.
- Hydrochloric AcidReacts with carbonate and sulfide ions to release gases, aiding in their identification.
- Magnesium SulfateDifferentiates between carbonate and bicarbonate ions by forming a precipitate only with carbonate.