Structural Formula definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackStructural Formula definitions
1/10
Terms in this set (10)
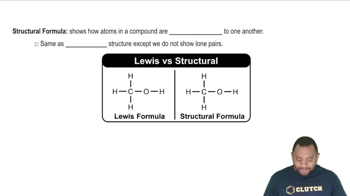
- Structural FormulaIllustrates how atoms are bonded in a molecule, omitting lone pairs, unlike Lewis structures.
- Molecular FormulaIndicates the ratio of elements in a compound but lacks connectivity information.
- ConnectivityDescribes how atoms are linked to each other in a molecule.
- OrientationRefers to the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule, relevant in stereoisomers.
- Lewis StructureDepicts atom connectivity and lone pairs in a molecule, unlike structural formulas.
- Lone PairsNon-bonding electron pairs shown in Lewis structures but omitted in structural formulas.
- C₂H₆OA molecular formula that can represent different structures like ethanol or dimethyl ether.
- EthanolA structural form of C₂H₆O with a hydroxyl group bonded to a carbon chain.
- Dimethyl EtherA structural form of C₂H₆O with an oxygen atom bonded between two methyl groups.
- Non-bonding ElectronsElectrons not involved in bonding, shown in Lewis structures but not in structural formulas.