Stoichiometry definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackStoichiometry definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- StoichiometryStudy of quantitative relationships in a balanced chemical equation to predict product amounts from reactants.
- Balanced Chemical EquationAn equation with equal numbers of each type of atom on both sides, crucial for stoichiometric calculations.
- MoleA unit representing 6.022 x 10^23 particles, used to convert between mass and number of particles in stoichiometry.
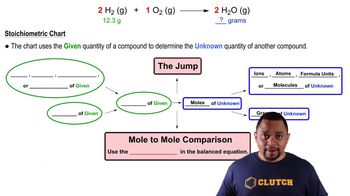
- Stoichiometric ChartA tool used to convert given quantities to unknown quantities through mole-to-mole comparisons.
- Given InformationThe initial quantity of a substance provided in a stoichiometric problem, often in grams or moles.
- Unknown InformationThe quantity of a substance to be determined in a stoichiometric problem, derived from given information.
- Mole-to-Mole ComparisonA step in stoichiometry using coefficients from a balanced equation to relate moles of reactants to products.
- CoefficientsNumbers in a chemical equation indicating the ratio of moles of each substance involved in the reaction.
- GramsA unit of mass used in stoichiometry to measure the given or unknown quantities of substances.
- AtomsThe smallest unit of an element, used in stoichiometry to express quantities of substances.
- MoleculesGroups of atoms bonded together, used in stoichiometry to express quantities of substances.
- IonsCharged particles formed when atoms gain or lose electrons, used in stoichiometry to express quantities.
- Formula UnitsThe lowest whole number ratio of ions in an ionic compound, used in stoichiometry to express quantities.
- JumpThe transition from moles of given to moles of unknown in stoichiometry, using a balanced equation.
- ConversionThe process of changing a quantity from one unit to another, such as grams to moles, in stoichiometry.