Precipitation: Ksp vs Q definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackPrecipitation: Ksp vs Q definitions
1/11
Terms in this set (11)
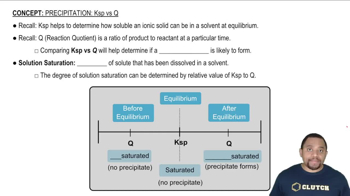
- KspThe solubility product constant indicating the maximum concentration of solute that can dissolve in a solvent at equilibrium.
- Reaction QuotientA ratio of the concentrations of products to reactants at a specific point in time, used to predict the direction of a reaction.
- PrecipitateA solid that forms in a solution when the reaction quotient exceeds the solubility product constant.
- Solution SaturationThe amount of solute dissolved in a solvent, determining whether a solution is unsaturated, saturated, or supersaturated.
- Unsaturated SolutionA solution where the reaction quotient is less than the solubility product constant, allowing more solute to dissolve.
- Saturated SolutionA solution at equilibrium where the reaction quotient equals the solubility product constant, with no net change.
- Supersaturated SolutionA solution where the reaction quotient is greater than the solubility product constant, leading to precipitate formation.
- EquilibriumA state where the forward and reverse reactions occur at the same rate, with no net change in concentrations.
- Ionic SolidA compound composed of ions that can dissociate into its constituent ions in a solvent.
- Forward DirectionThe direction in which a reaction proceeds to form more products, often when the reaction quotient is less than the solubility product constant.
- Reverse DirectionThe direction in which a reaction proceeds to form more reactants, often when the reaction quotient is greater than the solubility product constant.