Photoelectric Effect definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackPhotoelectric Effect definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
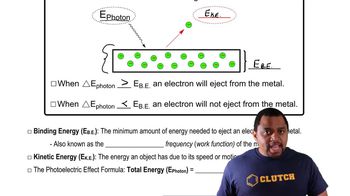
- Photoelectric EffectPhenomenon where photons with sufficient energy eject electrons from a metal surface.
- PhotonA particle representing a quantum of light or other electromagnetic radiation.
- ElectronA subatomic particle with a negative charge, ejected during the photoelectric effect.
- Metal SurfaceThe material from which electrons are ejected when struck by photons.
- Binding EnergyMinimum energy required to eject an electron from a metal surface.
- Threshold FrequencyThe minimum frequency of light needed to eject an electron from a metal.
- Work FunctionThe energy needed to remove an electron from a solid to a point in the vacuum.
- Kinetic EnergyEnergy an object possesses due to its motion, gained by ejected electrons.
- Planck's ConstantA fundamental constant used to describe the sizes of quanta, denoted as h.
- FrequencyThe number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time, denoted as mu.
- Electron VoltA unit of energy equal to approximately 1.602 x 10^-19 joules.
- JouleA derived unit of energy in the International System of Units.
- MassA measure of the amount of matter in an object, used in kinetic energy calculations.
- VelocityThe speed of something in a given direction, used in kinetic energy calculations.
- EnergyThe capacity to do work, involved in the ejection of electrons in the photoelectric effect.