Peroxide and Superoxide Reactions definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackPeroxide and Superoxide Reactions definitions
1/14
Terms in this set (14)
- PeroxideA compound containing an oxygen-oxygen single bond, often reacting to form hydrogen peroxide and hydroxide.
- SuperoxideA compound with an oxygen-oxygen bond, producing hydrogen peroxide and oxygen when reacting with water.
- Hydrogen PeroxideA product formed when peroxides or superoxides react with water or acids, known for its oxidizing properties.
- HydroxideA basic ion produced when peroxides react with water, forming part of the reaction's products.
- Barium PeroxideA peroxide that reacts with water to form barium hydroxide and hydrogen peroxide.
- Potassium SuperoxideA superoxide that reacts with water to produce potassium hydroxide, hydrogen peroxide, and oxygen.
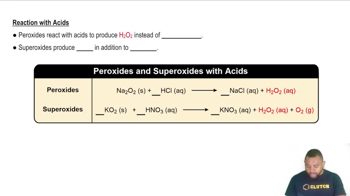
- Sodium PeroxideA peroxide that reacts with hydrochloric acid to form sodium chloride and hydrogen peroxide.
- Potassium NitrateA salt formed when potassium superoxide reacts with nitric acid, alongside hydrogen peroxide and oxygen.
- Oxygen GasA diatomic molecule produced as a byproduct in superoxide reactions with water or acids.
- OxideA compound of oxygen with another element, typically forming hydroxides when reacting with water.
- Hydrochloric AcidAn acid that reacts with sodium peroxide to produce sodium chloride and hydrogen peroxide.
- Nitric AcidAn acid that reacts with potassium superoxide to form potassium nitrate, hydrogen peroxide, and oxygen.
- SaltAn ionic compound formed as a product in reactions between peroxides or superoxides and acids.
- Balancing CoefficientsNumbers used to ensure the conservation of mass in chemical reactions, crucial for accurate reaction representation.