Periodic Trend: Electron Affinity definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackPeriodic Trend: Electron Affinity definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- Electron AffinityEnergy released when an electron is added to a gaseous atom, indicating exothermicity.
- Exothermic ReactionA process that releases energy, often resulting in a negative electron affinity.
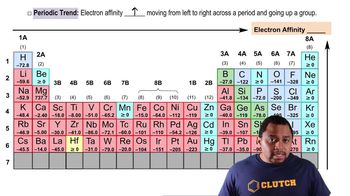
- Periodic TableA chart where electron affinity generally increases towards the top right corner.
- Gaseous AtomAn atom in the gas phase, often involved in electron affinity measurements.
- Negative ValueIndicates a stronger tendency to gain an electron in electron affinity.
- StabilityA condition where filled or half-filled orbitals resist accepting additional electrons.
- BerylliumAn element with a filled s orbital, showing reluctance to gain electrons.
- NitrogenAn element with half-filled p orbitals, contributing to its electron affinity exception.
- Noble GasesElements with complete outer shells, typically having zero or positive electron affinity.
- ZincAn element with filled d orbitals, showing resistance to electron gain.
- Half-filled OrbitalsA stable electron configuration that resists additional electron acceptance.
- Filled OrbitalsA stable electron configuration that resists additional electron acceptance.
- FluorineAn element with a high negative electron affinity, indicating a strong desire for electrons.
- CesiumAn element with a less negative electron affinity, indicating a weaker desire for electrons.
- KilojoulesThe unit of measurement for energy changes in electron affinity processes.