Periodic Table: Elemental Forms definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackPeriodic Table: Elemental Forms definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- MonoatomicElements stable as single atoms in nature, like lithium, magnesium, and zinc.
- DiatomicElements stable as pairs in nature, remembered by 'have no fear of ice cold beer'.
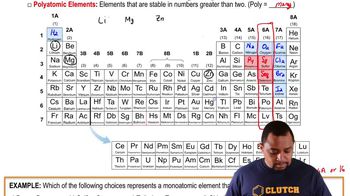
- PolyatomicElements stable in groups larger than two, such as phosphorus, sulfur, and selenium.
- HomonuclearCompounds composed of identical atoms, like H2, Cl2, P4, and S8.
- HeteronuclearCompounds composed of different atoms, such as water and carbon dioxide.
- LithiumA monoatomic element found stable as a single atom in nature.
- MagnesiumA monoatomic element stable as a single atom, not shaded red or blue on the periodic table.
- ZincA monoatomic element stable as a single atom, found naturally by itself.
- PhosphorusA polyatomic element existing as P4 in its most stable state in nature.
- SulfurA polyatomic element existing as S8, sharing group properties with selenium.
- SeleniumA polyatomic element existing as Se8, similar to sulfur due to group properties.
- HydrogenA diatomic element existing as H2, part of the mnemonic for diatomic elements.
- ChlorineA diatomic element existing as Cl2, part of the mnemonic for diatomic elements.
- BromineA diatomic element existing as Br2, part of the mnemonic for diatomic elements.
- IodineA diatomic element existing as I2, part of the mnemonic for diatomic elements.