Oxyacids definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackOxyacids definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- OxyacidA covalent compound with hydrogen ions bonded to polyatomic ions containing oxygen.
- Polyatomic ionAn ion composed of two or more atoms covalently bonded, acting as a single unit.
- Nitrite ionA polyatomic ion with the formula NO2-.
- Sulfite ionA polyatomic ion with the formula SO3^2-.
- Nitrous acidAn oxyacid with the formula HNO2, formed from nitrite ion.
- Sulfuric acidAn oxyacid with the formula H2SO3, formed from sulfite ion.
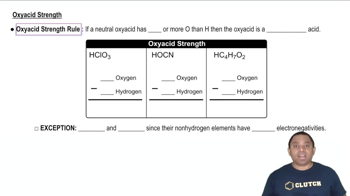
- Oxyacid strength ruleA rule stating that an oxyacid is strong if it has two or more oxygens than hydrogens.
- ElectronegativityA measure of an atom's ability to attract and hold electrons.
- Oxalic acidAn exception to the oxyacid strength rule, with low central element electronegativity.
- Iodic acidAn exception to the oxyacid strength rule, with low central element electronegativity.
- Hypoiodous acidAn oxyacid with fewer remaining oxygens compared to iodic acid.
- Central elementThe non-hydrogen element in an oxyacid, affecting its acidity.
- Group 6aA group in the periodic table containing oxygen, sulfur, and selenium.
- Remaining oxygensThe number of oxygens left after subtracting hydrogens in an oxyacid.
- AcidityThe strength of an acid, influenced by remaining oxygens and central element electronegativity.