Octet Rule definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackOctet Rule definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- Octet RuleA principle where main group elements aim for eight electrons in their valence shell for stability.
- Valence ElectronsElectrons in the outermost shell of an atom, determining its chemical bonding behavior.
- Covalent BondA chemical bond formed by the sharing of a pair of valence electrons between atoms.
- Noble GasesElements with a full valence shell, making them chemically inert and stable.
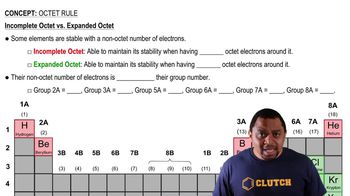
- Incomplete OctetA stable electron configuration with fewer than eight electrons in the valence shell.
- Expanded OctetA stable electron configuration with more than eight electrons in the valence shell.
- Group NumberA number indicating the column of an element in the periodic table, related to valence electrons.
- Main Group ElementsElements in groups 1, 2, and 13-18 of the periodic table, following the octet rule.
- Shared ElectronsElectrons that are shared between atoms in a covalent bond, contributing to the octet.
- Period 3 ElementsElements in the third row of the periodic table, capable of expanded octets.
- StabilityThe tendency of an atom to maintain a full or stable electron configuration.
- Chemical BondingThe process by which atoms combine to form molecules, achieving stable electron configurations.
- Electron ShellA grouping of electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom, defining its energy level.
- HydrogenAn element that achieves stability with only two electrons, an exception to the octet rule.
- BerylliumAn element stable with four valence electrons, not conforming to the octet rule.