Molecular Geometry definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackMolecular Geometry definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- Molecular GeometryThe true shape of a molecule considering repulsion between lone pairs and bonded atoms.
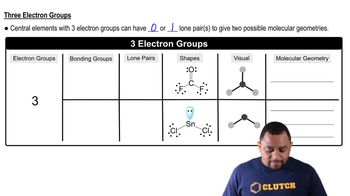
- Electron GroupsThe total number of lone pairs and bonded atoms around a central atom.
- Lone PairsPairs of valence electrons not involved in bonding, affecting molecular shape.
- Bonding GroupsAtoms bonded to a central atom, contributing to the molecule's geometry.
- LinearGeometry with two electron groups and no lone pairs, forming a straight line.
- Trigonal PlanarGeometry with three electron groups and no lone pairs, forming a flat triangle.
- BentGeometry with two bonding groups and one or two lone pairs, forming an angular shape.
- TetrahedralGeometry with four bonding groups and no lone pairs, forming a pyramid-like shape.
- Trigonal PyramidalGeometry with three bonding groups and one lone pair, resembling a pyramid.
- Trigonal BipyramidalGeometry with five bonding groups and no lone pairs, forming two stacked pyramids.
- SeesawGeometry with four bonding groups and one lone pair, resembling a seesaw.
- T-ShapedGeometry with three bonding groups and two lone pairs, forming a T shape.
- OctahedralGeometry with six bonding groups and no lone pairs, forming an eight-faced shape.
- Square PyramidalGeometry with five bonding groups and one lone pair, forming a square-based pyramid.
- Square PlanarGeometry with four bonding groups and two lone pairs, forming a flat square shape.