Lewis Dot Structures: Acids definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackLewis Dot Structures: Acids definitions
1/13
Terms in this set (13)
- Covalent CompoundA chemical compound where atoms are bonded by shared pairs of electrons, typically involving nonmetals.
- Hydronium IonA positively charged ion formed when a hydrogen ion bonds with a water molecule, often represented as H+.
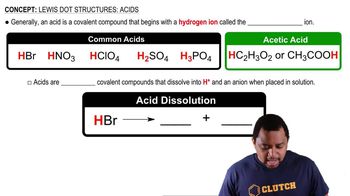
- Hydrobromic AcidA strong acid composed of hydrogen and bromine, dissociating into H+ and Br- ions in solution.
- Nitric AcidA strong acid with the formula HNO3, known for its ability to dissociate into H+ and NO3- ions.
- Hydrochloric AcidA strong acid consisting of hydrogen and chlorine, dissociating into H+ and Cl- ions in solution.
- Sulfuric AcidA strong acid with the formula H2SO4, dissociating into H+ and SO4^2- ions in solution.
- Phosphoric AcidA moderate acid with the formula H3PO4, dissociating into H+ and PO4^3- ions in solution.
- Acetic AcidA weak acid with the formula CH3COOH, can be represented with hydrogen at the beginning or within the formula.
- DissociationThe process by which a compound breaks into ions when dissolved in a solution.
- AnionA negatively charged ion that results from the dissociation of an acid in solution.
- SolubleA property of a substance that allows it to dissolve in a solvent, forming a solution.
- Chemical ReactionA process that involves the rearrangement of molecular or ionic structure of a substance.
- Acid-Base TitrationA laboratory method to determine the concentration of an acid or base by neutralizing it with a standard solution.