Lewis Acids and Bases definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackLewis Acids and Bases definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- Lewis AcidAn entity that accepts an electron pair, often a positively charged ion or a molecule with less than eight valence electrons.
- Lewis BaseA substance that donates an electron pair, typically characterized by a lone pair or a negative charge.
- Electron Pair AcceptorA characteristic of Lewis acids, involving the acceptance of an electron pair to form a bond.
- Electron Pair DonorA feature of Lewis bases, involving the donation of an electron pair to form a bond.
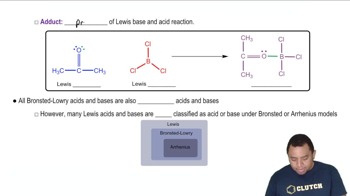
- AdductThe product of a Lewis acid-base reaction, formed by the combination of the acid and base.
- Octet RuleA principle stating that atoms tend to bond in a way that gives them eight valence electrons.
- Valence ElectronsElectrons in the outermost shell of an atom, crucial for forming chemical bonds.
- Transition MetalsElements that can accept electron pairs due to their d orbitals, often acting as Lewis acids.
- Lone PairA pair of valence electrons not involved in bonding, often found in Lewis bases.
- Positive ChargeAn indicator of a Lewis acid, often seen in metal ions or H+ ions.
- Negative ChargeAn indicator of a Lewis base, suggesting an excess of electrons available for donation.
- BoronA group 3A element that can act as a Lewis acid due to having only six valence electrons.
- Magnesium ChlorideA compound where magnesium acts as a Lewis acid due to its electron deficiency.
- Aluminum BromideA compound where aluminum acts as a Lewis acid, having fewer than eight valence electrons.
- AcetoneA molecule that can act as a Lewis base by donating a lone pair of electrons.