Intro to Redox Reactions definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackIntro to Redox Reactions definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- Redox ReactionsInvolve electron transfer between reactants, altering oxidation states.
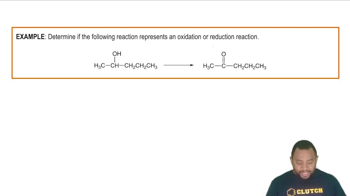
- OxidationIncreases carbon-oxygen bonds, transforming alcohols to aldehydes or ketones.
- ReductionIncreases carbon-hydrogen bonds, converting carboxylic acids to alcohols.
- Carbon-Oxygen BondsIncrease during oxidation, indicating a higher oxidation state.
- Carbon-Hydrogen BondsIncrease during reduction, indicating a lower oxidation state.
- AlcoholsOrganic compounds that can be oxidized to aldehydes or ketones.
- AldehydesIntermediate oxidation products between alcohols and carboxylic acids.
- KetonesSimilar to aldehydes, formed during oxidation of secondary alcohols.
- Carboxylic AcidsResult from further oxidation of aldehydes, containing three carbon-oxygen bonds.
- HydrocarbonsCompounds with only carbon and hydrogen, not central in redox reactions.
- Carbon DioxideEnd product of complete oxidation, not typically involved in organic redox.
- Functional GroupsSpecific groups of atoms within molecules that determine chemical reactions.
- Organic ChemistryBranch of chemistry focusing on carbon-containing compounds and their transformations.
- Electron TransferMovement of electrons from one reactant to another in redox reactions.
- Oxidation StateIndicates the degree of oxidation of an atom in a chemical compound.