Integrated Rate Law definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackIntegrated Rate Law definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- Integrated Rate LawDescribes the relationship between reactant concentrations and time, varying with reaction order.
- Zero Order ReactionReaction where concentration decreases linearly over time, with rate constant units of molarity per time.
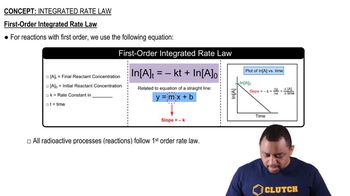
- First Order ReactionReaction where the natural logarithm of concentration versus time is linear, with rate constant units of time inverse.
- Second Order ReactionReaction where the inverse of concentration versus time is linear, with rate constant units of molarity inverse per time.
- Rate ConstantA proportionality constant in rate laws, with units dependent on the reaction order.
- Reaction OrderDetermines the power to which the concentration of a reactant is raised in the rate law.
- MolarityA measure of concentration, expressed as moles of solute per liter of solution.
- Natural LogarithmThe logarithm to the base e, used in first order reaction rate equations.
- Radioactive ProcessA process that follows first order kinetics, often involving decay of isotopes.
- SlopeIn rate law graphs, represents the rate constant, negative for zero and first order, positive for second order.
- ConcentrationThe amount of a substance in a given volume, crucial in determining reaction rates.
- Time InverseUnits of rate constant for first order reactions, indicating per unit time.
- PlotA graphical representation of data, used to identify reaction order by the relationship between variables.
- Initial ConcentrationThe concentration of reactants at the start of a reaction, denoted as a sub 0.
- Final ConcentrationThe concentration of reactants at a given time during a reaction, denoted as a sub t.