Halogenation Reactions definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackHalogenation Reactions definitions
1/10
Terms in this set (10)
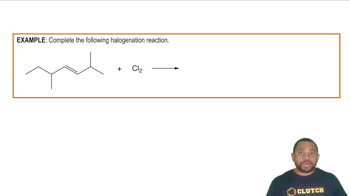
- HalogenationA reaction involving the addition of halogens to unsaturated hydrocarbons, transforming them into more reactive compounds.
- AlkeneA hydrocarbon containing a carbon-carbon double bond, which can undergo halogenation to form dihalides.
- AlkyneA hydrocarbon with two carbon-carbon pi bonds, requiring two moles of halogen for complete halogenation.
- Pi bondA type of covalent bond formed by the sideways overlap of p orbitals, present in alkenes and alkynes.
- DihalideA compound formed when two halogen atoms are added to an alkene during halogenation.
- TetrahalideA compound resulting from the addition of four halogen atoms to an alkyne in a halogenation reaction.
- ReagentA substance or compound added to a system to cause a chemical reaction, such as halogens in halogenation.
- BromineA halogen element used in halogenation reactions to add to pi bonds in alkenes and alkynes.
- ChlorineA halogen element that can react with alkenes and alkynes to form dihalides and tetrahalides.
- Unsaturated hydrocarbonA hydrocarbon with one or more pi bonds, capable of undergoing halogenation to form halogenated compounds.