Functional Groups in Chemistry definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackFunctional Groups in Chemistry definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
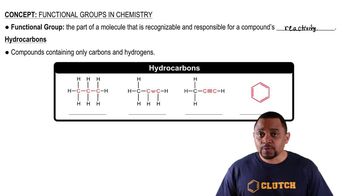
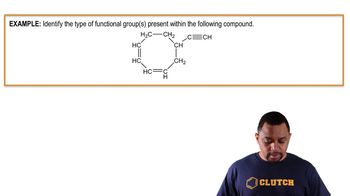
- HydrocarbonsCompounds composed solely of carbon and hydrogen atoms, forming the basis of organic chemistry.
- AlkanesHydrocarbons with single carbon-carbon bonds, characterized by their saturated nature.
- AlkenesHydrocarbons containing at least one carbon-carbon double bond, making them unsaturated.
- AlkynesHydrocarbons with one or more carbon-carbon triple bonds, known for their linear geometry.
- Aromatic ringsRing structures with alternating double and single bonds, exemplified by benzene.
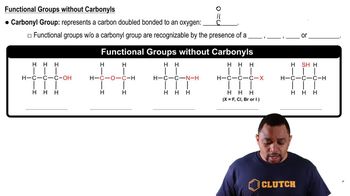
- AlcoholsOrganic compounds with a hydroxyl group (OH) attached to a saturated carbon atom.
- EthersCompounds with an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups, forming a C-O-C linkage.
- AminesOrganic compounds derived from ammonia, containing a nitrogen atom bonded to hydrogen or carbon.
- Alkyl halidesCompounds where a halogen atom is bonded to an alkyl group, represented as C-X.
- ThiolsOrganic compounds containing a sulfhydryl group (SH) attached to a carbon atom.
- Carboxylic acidsOrganic acids with a carbonyl group bonded to a hydroxyl group, denoted as C=O-OH.
- EstersDerived from carboxylic acids, featuring a carbonyl group bonded to an oxygen atom linked to another carbon.
- AmidesCompounds with a carbonyl group directly bonded to a nitrogen atom, forming C=O-N.
- AldehydesOrganic compounds with a carbonyl group bonded to at least one hydrogen atom, denoted as C=O-H.
- KetonesCompounds with a carbonyl group flanked by two carbon atoms, forming a C=O linkage.