Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackEndothermic & Exothermic Reactions definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
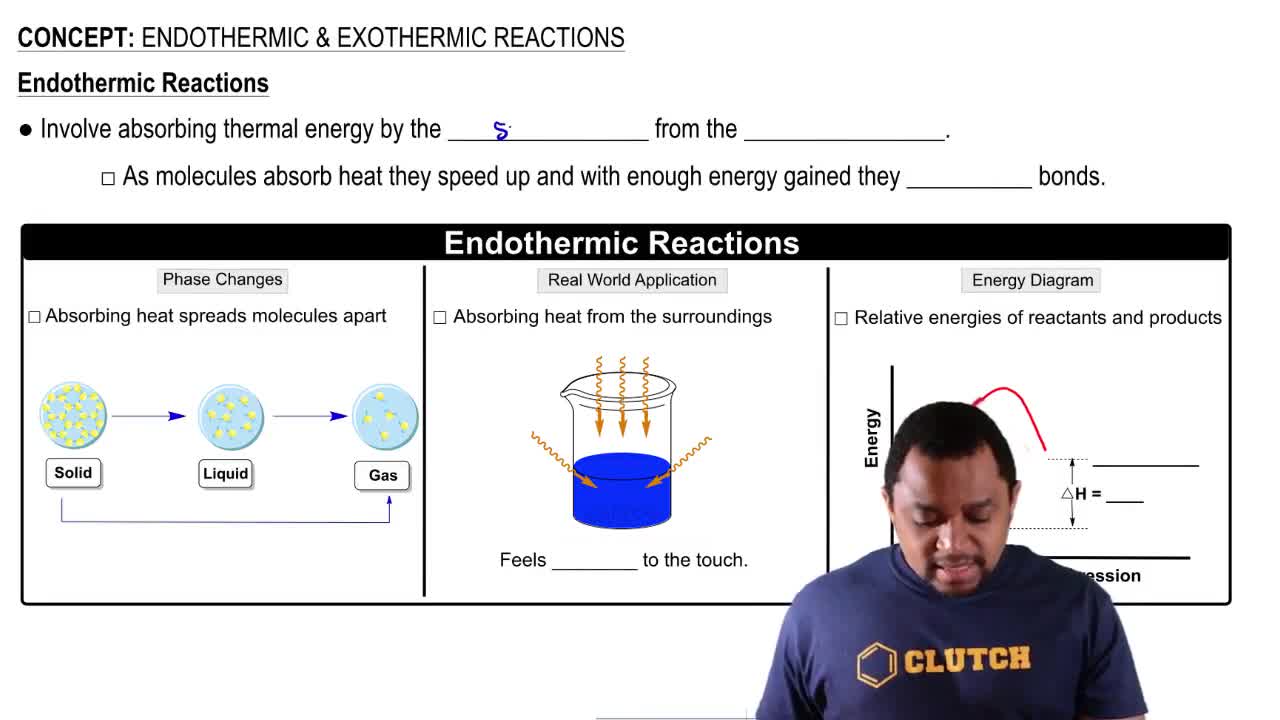
- Endothermic ReactionA process that absorbs thermal energy, causing molecules to speed up and break bonds, often feeling cold to the touch.
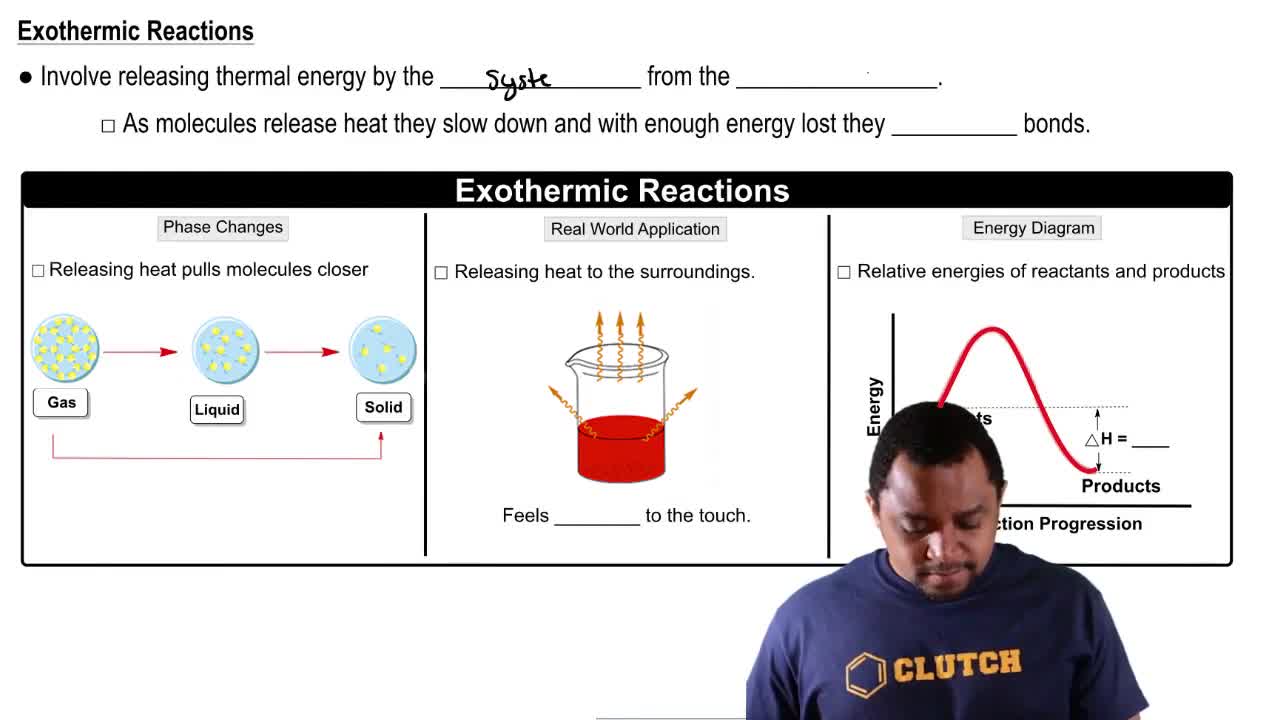
- Exothermic ReactionA process that releases thermal energy, causing molecules to slow down and form bonds, often feeling warm to the touch.
- Thermal EnergyThe energy absorbed or released during chemical reactions, affecting molecular motion and phase changes.
- Phase ChangeA transition between different states of matter, such as solid, liquid, and gas, influenced by thermal energy.
- FusionThe process of a solid absorbing heat to become a liquid, also known as melting.
- VaporizationThe process of a liquid absorbing heat to become a gas.
- SublimationThe transition of a solid directly into a gas without passing through the liquid phase.
- CondensationThe process of a gas releasing heat to become a liquid.
- FreezingThe process of a liquid releasing heat to become a solid.
- DepositionThe transition of a gas directly into a solid without passing through the liquid phase.
- Energy DiagramA graphical representation showing the energy changes during a chemical reaction.
- EnthalpyA measure of heat change in a reaction, positive for endothermic and negative for exothermic processes.
- Delta HThe symbol representing the change in enthalpy during a chemical reaction.
- ReactantsThe starting substances in a chemical reaction, typically at a higher energy level in exothermic reactions.
- ProductsThe substances formed in a chemical reaction, typically at a higher energy level in endothermic reactions.