Electron Configurations of Transition Metals: Exceptions definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackElectron Configurations of Transition Metals: Exceptions definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
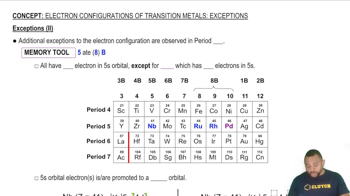
- Transition MetalsElements in the d-block of the periodic table, known for having variable oxidation states.
- Electron ConfigurationThe distribution of electrons in an atom's orbitals, crucial for understanding chemical properties.
- ChromiumA transition metal with atomic number 24, known for its electron configuration exception.
- Atomic NumberThe number of protons in an atom's nucleus, determining its position in the periodic table.
- S OrbitalA spherical electron orbital, capable of holding up to two electrons.
- D OrbitalA set of five orbitals in the d-block, each capable of holding two electrons.
- Half-filled OrbitalsA stable electron configuration where each orbital in a subshell has one electron.
- PalladiumA transition metal with a unique electron configuration, lacking electrons in its 5s orbital.
- NiobiumA transition metal with an electron configuration exception, promoting an electron to the d orbital.
- ArgonA noble gas used as a reference point in electron configurations for transition metals.
- KryptonA noble gas used as a reference in electron configurations, preceding transition metals like Niobium.
- Period 5The fifth row of the periodic table, containing elements with notable electron configuration exceptions.
- Group 5BA group in the periodic table containing transition metals with electron configuration exceptions.
- Group 8BA group in the periodic table with transition metals exhibiting unique electron configurations.
- Electron PromotionThe process of moving an electron from a lower energy orbital to a higher one, often seen in exceptions.