Combustion Analysis definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackCombustion Analysis definitions
1/13
Terms in this set (13)
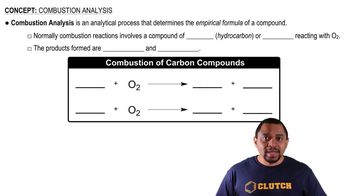
- Combustion AnalysisA method to determine a compound's empirical formula by analyzing combustion reaction products.
- Empirical FormulaThe simplest whole-number ratio of atoms in a compound.
- HydrocarbonA compound composed solely of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
- Carbon DioxideA gaseous product of combustion reactions involving carbon-containing compounds.
- WaterA product formed in combustion reactions involving hydrogen-containing compounds.
- Oxygen GasA reactant in combustion reactions, often denoted as O2.
- OctaneA hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C8H18, used as a fuel.
- GlucoseA compound with the formula C6H12O6, containing carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
- Sulfur DioxideA gaseous product formed in combustion reactions involving sulfur.
- Nitrogen DioxideA gaseous product formed in combustion reactions involving nitrogen.
- Diatomic MoleculesMolecules composed of two atoms, such as F2, Cl2, Br2, and I2.
- HalogensElements in group 7A, including fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine.
- Non-HydrocarbonA compound containing carbon, hydrogen, and other elements like sulfur or nitrogen.