Chirality definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackChirality definitions
1/10
Terms in this set (10)
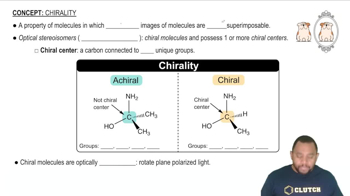
- ChiralityA property of molecules where mirror images are non-superimposable, often due to a carbon atom bonded to four different groups.
- EnantiomersChiral molecules that are mirror images of each other and rotate plane-polarized light.
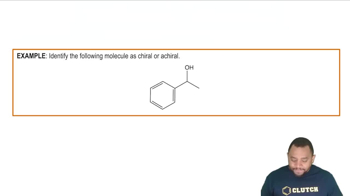
- Chiral CenterA carbon atom bonded to four unique groups, making the molecule chiral.
- Optical IsomersAnother term for enantiomers, highlighting their ability to rotate plane-polarized light.
- AchiralDescribes a molecule that lacks a chiral center, having no four unique groups attached to a carbon.
- Plane-Polarized LightLight that vibrates in a single plane, used to observe optical activity in chiral molecules.
- IsomersMolecules with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements.
- Mirror ImageA reflection of a molecule that may or may not be superimposable on the original.
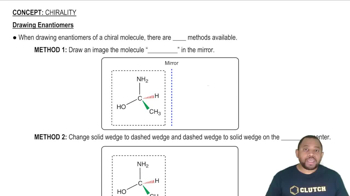
- Inversion MethodA technique to draw enantiomers by changing the spatial orientation of bonds.
- Dash-Wedge BondA representation of three-dimensional molecular structures, indicating bond direction.