Bond Angles definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackBond Angles definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
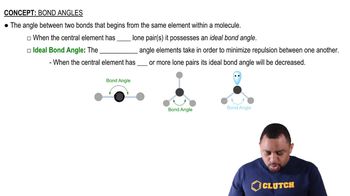
- Bond angleThe angle between two bonds originating from the same central atom in a molecule.
- Central atomAn atom in a molecule from which bonds to surrounding atoms originate.
- Lone pairA pair of valence electrons not shared with another atom, affecting bond angles by increasing repulsion.
- Ideal bond angleThe optimal angle between bonds that minimizes electron repulsion when no lone pairs are present.
- Electron groupA set of electrons around a central atom, including bonds and lone pairs, influencing molecular shape.
- Linear shapeA molecular shape with two electron groups and a bond angle of 180 degrees.
- Trigonal planarA molecular shape with three electron groups and a bond angle of 120 degrees.
- Equatorial positionPositions around a central atom in a trigonal bipyramidal shape, typically with 120-degree bond angles.
- Axial positionPositions in a trigonal bipyramidal shape, typically with 90-degree bond angles to equatorial positions.
- Trigonal bipyramidalA molecular shape with five electron groups, having both equatorial and axial bond angles.
- TetrahedralA molecular shape with four electron groups and an ideal bond angle of 109.5 degrees.
- Bent shapeA molecular shape resulting from lone pairs reducing bond angles from their ideal values.
- OctahedralA molecular shape with six electron groups, typically having 90-degree bond angles.
- RepulsionThe force that pushes electron groups apart, affecting bond angles in a molecule.
- Molecular geometryThe three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule, influenced by bond angles and lone pairs.