Bohr Equation definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackBohr Equation definitions
1/10
Terms in this set (10)
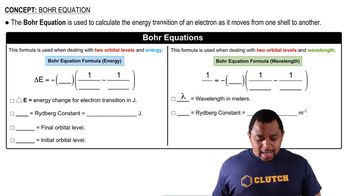
- Bohr EquationCalculates energy transition of an electron between atomic shells using Rydberg constant.
- Energy TransitionChange in energy when an electron moves between different orbital levels.
- Rydberg ConstantA constant used in Bohr equations, 2.178 x 10^-18 J for energy, 1.0974 x 10^7 m^-1 for wavelength.
- Principal Quantum NumberDenoted as 'n', represents the electron's orbital level or shell.
- Orbital LevelSpecific energy level of an electron in an atom, indicated by the principal quantum number.
- WavelengthDistance between successive peaks of a wave, related to energy transitions in Bohr's second equation.
- Spectral LinesDistinct lines representing wavelengths of light emitted or absorbed by electrons in atoms.
- Quantum MechanicsBranch of physics dealing with the behavior of electrons and other particles at atomic scales.
- Atomic StructureArrangement of electrons around the nucleus of an atom, explained by Bohr's model.
- Electron BehaviorMovement and energy changes of electrons within an atom, described by quantum mechanics.